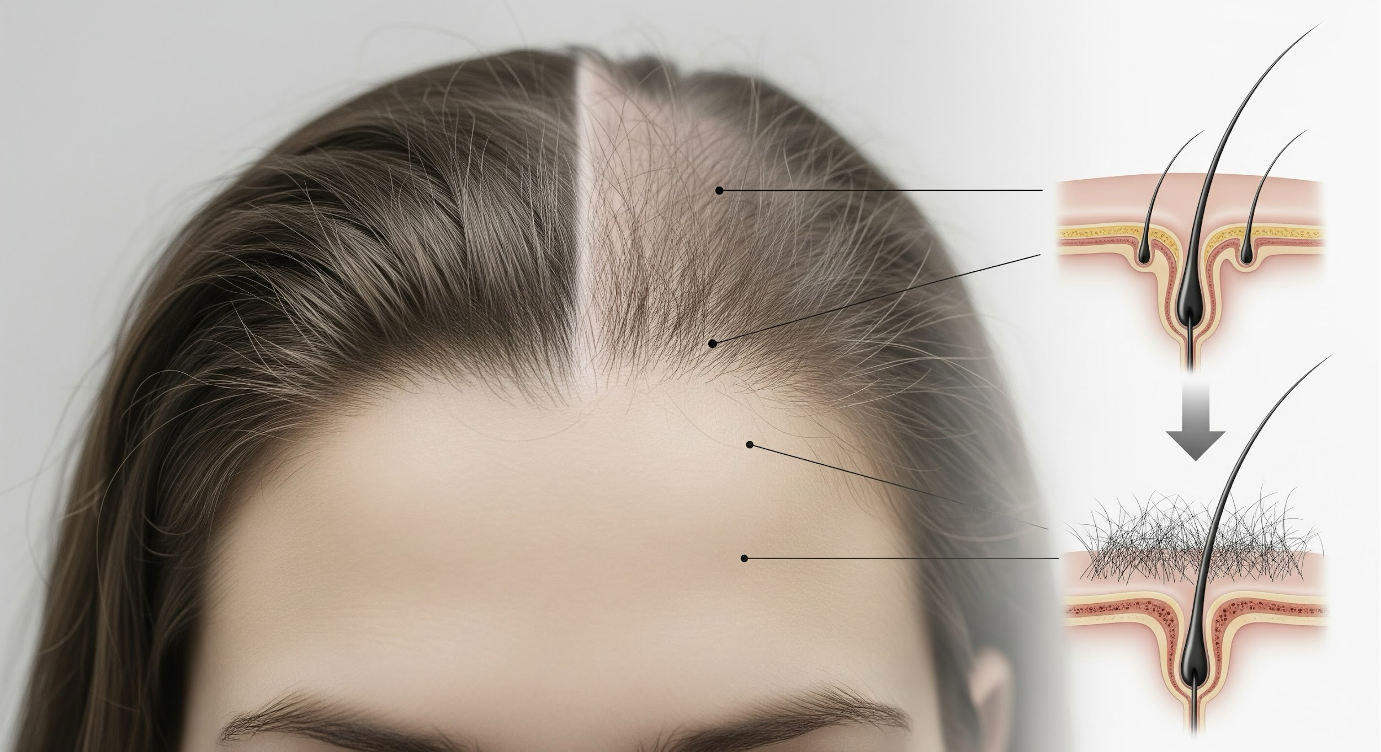
The marketplace for hair restoration solutions overflows with bold claims and miracle cures, leaving many consumers confused about what actually delivers results. Separating scientific fact from marketing fiction reveals several evidence-based approaches, from topical treatments like minoxidil to advanced procedures like FUE treatment, each with distinct mechanisms and success rates. Below, we examine the science behind the most widely used options.
Minoxidil
As the only topical treatment approved by the FDA, minoxidil remains the benchmark against which other options are measured. Originally developed as a blood pressure medication, its hair growth side effect led to repurposing. The liquid or foam formulation works by vasodilation, potentially prolonging growth phases in susceptible follicles. However, results vary widely – some users experience significant regrowth while others see only maintenance of existing hair. Discontinuation typically leads to reversal of benefits within months.
Finasteride
This oral medication inhibits 5-alpha reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone to follicle-damaging DHT. Clinical studies demonstrate impressive results for male pattern baldness, with over 80% of users maintaining or improving hair counts. However, potential sexual side effects – though statistically uncommon and often reversible – create understandable hesitation. Lower doses may offer similar benefits with reduced risk, though long-term data remain limited.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
This in-office procedure involves drawing blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and reinjecting the plasma into the scalp. Growth factors in platelets may stimulate dormant follicles. While studies show promise, particularly for early-stage loss, results remain inconsistent. The treatment requires multiple initial sessions and ongoing maintenance, with costs accumulating quickly since insurance rarely covers the procedure.
Low-Level Laser Therapy Devices
FDA-cleared laser caps and combs claim to stimulate follicles through photobiomodulation. Research suggests modest benefits, primarily in slowing loss rather than dramatic regrowth. Consistent use (typically 3-4 times weekly) appears necessary to maintain effects. While convenient, high-quality devices require significant investment with variable individual results.
Natural Remedies
Rosemary oil has emerged as perhaps the most promising plant-based option, with studies showing comparable efficacy to low-dose minoxidil for mild cases. Saw palmetto may offer mild DHT-blocking effects, while pumpkin seed oil shows potential in preliminary research. These gentler alternatives appeal to those avoiding pharmaceuticals, though results take longer to manifest.
Supplements
While correcting nutritional deficiencies can improve hair health, most commercial “hair growth” supplements offer little benefit for well-nourished individuals. Biotin only helps those deficient in the vitamin, while collagen supplements face limited absorption issues. Targeted blood testing can identify specific deficiencies worth addressing.
Hair Transplantation
Surgical options provide the most dramatic transformations for qualified candidates, but misconceptions abound. Modern techniques create natural-looking results when performed by skilled surgeons, though the procedure doesn’t prevent ongoing loss in untreated areas. Not everyone makes an ideal candidate – sufficient donor hair must exist for harvesting grafts.
Combination Approaches
The most successful strategies typically layer multiple modalities. A morning application of minoxidil followed by evening rosemary oil, combined with weekly microneedling and bi-monthly PRP sessions, creates a comprehensive approach. This multi-target strategy addresses various pathways simultaneously for cumulative benefits.
Managing Expectations
Hair restoration remains an imperfect science with no universal solutions. Genetic factors influence individual responses, and visible improvements typically require months of consistent treatment. Consulting a dermatologist helps create personalised plans based on specific hair loss patterns and causes.
The evidence clearly shows that while no perfect solution exists, several options offer genuine help for thinning hair. From clinically proven pharmaceuticals to emerging natural approaches, today’s treatments provide more hope than ever for maintaining and restoring hair. The key lies in matching interventions to individual needs while maintaining realistic expectations about outcomes.




